What Is Synesthesia? And Are You Aware Of Your Synesthetic Abilities?
What if you have Synesthesia, the ability to see Music in shapes and colors? Or to smell textures? Or to touch colors?
What if you have synesthesia and you are not aware of it?
Maybe letters and numbers are colored personalities? And is your week is arranged as a shape in your mental space?
Maybe you are a synesthete, and you did not even notice it.
Discover Your Synesthesia
What is synesthesia? In this article, you will get an overview of the fascinating world of synesthesia. There is a lot to discover and to learn.
You will learn:
- What is Synesthesia?
- Different Types of Synesthesia
- What are the genetic and neuronal basics?
- What are the benefits of having synesthesia?
- How to become aware of the synesthetic gift.
And you may be surprised how many benefits there are, when aware of synesthesia. It may change the way you perceive the world.
Synesthesia: the blending of the senses
Wikipedia defines synesthesia as following:
Well, that is a beautiful definition of synesthesia, but what does it mean?
Co-activation of different sensory areas in the brain
Synesthesia derives from Greek. “Syn” stands for together, “esthesia” means perception. Loosely translated it means perceiving together. The word “Anesthesia” is the opposite: no perception.
Synesthesia is a condition where one sense co-activates other senses.
Okay, “condition” sounds clinical. It is instead a gift, and it has nothing to do with a disease or a mental disorder. You also do not need any medication or medical treatment.
Scientists just like to have a word for it, that is as neutral as possible. So they call it condition.
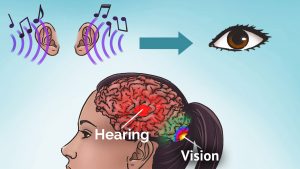
Synesthesia is more common than previously assumed!
There are many people with synesthesia that are not aware of it. They miss the beauty and the benefits of Synesthesia.
You experience synesthesia when you give attention to it. But in our modern society, we are wrapped up in thoughts about the past and the future. Often we miss being aware of the sensations of the present moment.
Meditation Cultivates Synesthesia
A study points out that meditators may be more aware of synesthetic experiences. It is not a surprise. The goals of meditation are to increase the sensory sensitivity.
Mindfulness is to experience the present moment with sustained attention. To be more aware of the present moment.
The Synesthesia Research pioneers Prof. Eagleman and Prof. Cytowic put it in this way:
Learn to meditate if you hope to experience Synesthesia
Maybe you resonate with Synesthesia, too! In the Sensorium, you find over 150 exercises to discover and familiarize with different types of synesthesia.
Synesthesia Meditation For Free
Synesthesia Mediation: Discover your synesthetic abilities
Watch our Video
Synesthesia Meditation – synesthetic Mindfulness for sensory Awareness
Guided Synesthesia Meditation is a combination of mindfulness exercises and synesthetic explorations. Practice 10 minutes per day. Increase your synesthetic mindfulness* and sensory awareness. Find better sleep, increase feelings of calm, relaxation and balance, while decreasing stress, and gaining improved focus and life quality. Over 150 exercises are available on https://synesthesia.com.
With a free account, you can save the progress of your synesthetic journey!
Synesthesia Is Perceiving the World With Blended Senses.
Music can be colored, letters and figures can be associated with genders and personality, and forms can have tastes. There are many different types of synesthesias; every sense can theoretically be coupled with any other sense. Synesthesia is not the product of imagination or hallucination.
It is the result of enhanced neuronal connections.
Do you resonate with Synesthesia?
Are you up for a Synesthesia Tests? They are according to the “gold-standard” of testing synesthesia. However, take the results with a grain of salt.
Stronger Neurological Connections Between Sensory Areas
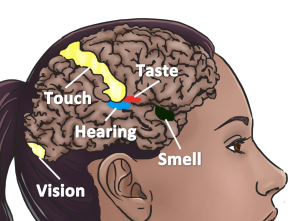 . Meaning, Music is the inducer and it co-activates the Colors, the concurrent.
. Meaning, Music is the inducer and it co-activates the Colors, the concurrent.
Another example is the personification of a letter. The letter is the inducer, the perception of a personification is the concurrent. Short: Letter -> personification.
Using this terminology allows the researchers to be more concise communicating and writing about different types of synesthesia.
Some common types of Synesthesia
There are many different types of synesthesia. Some are more common than others. Here you get an overview of the most “famous” ones. If you want to go in depth, read the article “types of synesthesia”.
Meditation is an excellent channel to explore the different types of synesthesia.
Do you prefer to try to experience synesthesia than merely reading about it? So check out the free synesthetic exercises in the Gateway.
Grapheme-color synesthesia: perceiving letters and numbers in colors.
Spatial sequence synesthesia spatiotemporal synesthesia: perceiving the alphabet, or calendar units such as the year or a week as shapes in space.
Number form: The numbers are arranged in a mental space.
Chromesthesia: The perception of music in shapes and colors

Auditory-tactile synesthesia: you hear something, and you can touch it.
Ordinal linguistic personification (OLP): perceiving letters and numbers as personalities
Mirror-Touch Synesthesia & Mirror-Pain Synaesthesia: Seeing somebody being touched or in pain and then perceiving it as well.
Lexical-Gustatory Synesthesia: words or numbers have a taste.

Tastes and smells evoke the sensation of shapes and colors.
The subtlety of synesthesia – do not miss it!
Synesthetic experiences can be very subtle. For many people, it is hidden in daily life. Synesthetic experiences require attention and focus. Some types of synesthesia are more accessible to perceive, such as the colors of letters and numbers, than, let’s say the taste of color.
Synesthetic perceptions “out in space.”

Synesthetic perceptions are often perceived somewhere in space. Synesthetes state that it is as if they were looking at it. Music played with a loudspeaker may be seen externally. While the colors of music with headphones may be perceived are somewhat in mind.
Letter “A” in red? That is ugly!
The synesthetic experiences are consistent. So for me, letter “A” is blue, and it has always been blue. And probably it will stay blue forever. Though maybe for you, the letter “A” in blue may be ugly and unpleasant experience.
That the colors are consistent but different for everybody is called “idiosyncrasy.” For everybody it is different, but it remains the same.
Synesthetes can have never-ending discussions about whether letter A is better in blue or in red.
For a synesthete seing a wrong colored letter, it may feel uncomfortable. Like the word “green” written in red.

Also, the synesthetic experiences may vary between people with synesthesia. Some rather associate the colors to a letter, others instead see the colors directly on the letters.
These are associator synesthetes and projector synesthetes, respectively.
What color is Letter A for you? How do you like letter A in blue? Do you perceive the color rather in your mental space or directly on the page? Check out our free mindful synesthetic exercises in the gateway (for free!).
Free Synesthetic Activities
Or read our article about Color-Grapheme Synesthesia.
What color is Tuesday? Exploring synesthesia – Richard E. Cytowic
View full lesson: http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-color-is-tuesday-exploring-synesthesia-richard-e-cytowic How does one experience synesthesia — the neurological trait that combines two or more senses? Synesthetes may taste the number 9 or attach a color to each day of the week. Richard E. Cytowic explains the fascinating world of entangled senses and why we may all have just a touch of synesthesia.
Genetics and learning; the cause of Synesthesia?
A study about the familial patterns of synesthesia showed that 42% of the participants have a first-degree relative with synesthesia. Some years ago, a research team scanned families with and without synesthetes genetically.
Several genetic regions of the DNA could be detected that may relate to synaesthesia. These “synesthesia” genes are located on different chromosomes and may be involved in the development of the brain. It seems to be quite complicated.
Breaking news for Synesthesia and Genetics in 2018
A newer study investigated the DNA of families with and without Synesthesia. They used new technologies that could sequence (study) all genes the encode for proteins.
They found 37 genes that predict is there is synesthesia in a family or not. But they also concluded that there is not just one “synesthesia gene.”
Some of these genes participate in axonal growth. Or in other words, they help neurons to connect to each other. What fits nicely into the theory of increased connections between sensory areas such as the auditory and visual cortex. They play a role in childhood.
But additional factors than genetics do play a role.
Studies ran on monozygotic twins found that they have different types of synesthesia. If it was purely genetic, then twins should have the same types of synesthesia. More genetic research is being done at the moment. We wait with anticipation for the outcome.
One hypothesis is that synesthesia develops in the period after birth – also called neonatal phase of a child. The brain of freshly born children are still a “mess”. It could be that the life of everybody begins with a form of synesthesia and for some this ability remains.
Another hypothesis proposes, that learning could influence the development of synesthesia. It could be that synesthesia forms as a reaction to learning challenges in early childhood.
Though synesthetes state that they have had the colors for the letters since they are children, it seems that it takes time for synesthesia to form.
If you want to read more about the brain, genetics and the development of synesthesia, read our article about the research on synesthesia, science, and the brain.
Cognitive advantages of synesthesia
“Synesthesia is associated with many cognitive benefits. Synesthetes may be more creative, have better perception, better memories and are gifted in many ways.”
The science of synesthesia, memory and the cognitive advantages is still in its infancy. But more and more evidence and insights about the advantages of synesthesia are being revealed.
There are some studies about memory showing that synesthetes may perform better in tasks involving graphemes (letters and numbers) than non-synesthetes. Though such findings were not in all studies. Nevertheless, some studies reported impressive advantages.
Creativity
Creativity is the process of generating novel associations. A study has demonstrated that people with synaesthesia are more likely to be engaged in the creative arts.
And they score higher on some, but not all, tests of creativity.
When questioned, 24% of synesthetes are employed in an artistic profession, whereas in the non-synesthete population this applies to only 2%.
Creativity is not only a property that is required to work in the arts. Many other professions, such as science, involve creative thinking.
It seems as if due to the “synesthetic cross connections” different concepts are easier combined, leading to an improved thinking. Some scientists go even so far, that they say the synesthesia gene may have evolved due to improved creativity. But this is only a hypothesis.
Both synesthesia and mindfulness meditation are independently associated with increased creativity. What may happen if you put Synesthesia and Meditation together? 😉
Memory advantages increased intelligence and linguistic aid

Synesthetes also tend to have a “superior” memory. But some scientists prefer to name it “alternative learning strategies.” Being a synesthete does not make you a savant.
Dealing with the “co-activated senses” can provide a memory advantage. For example a letter – color synesthete may have an advantage in color memory. Or synesthetes with calendar form synesthesia show visual short-term memory advantages.
But it also goes the other way around. Letter – color synesthetes show advantages for different memory tasks which involve lists or words.
Some studies suggest that they are better at learning an artificial grammar. Calendar–form synesthetes also show better autobiographical and somewhat better historical memories.

Does synesthesia help to learn new scripts such as Hebrew?
One study showed that the synesthetic colors are transferred to other scriptures. So learning a language with different letters may be more comfortable when the new symbols take over the corresponding colors of the Latin system.
This transformation of synesthetic colors from one script to another is called cross-linguistic transfer.

Maybe everybody can train synesthesia and benefit
Nicolas Rothen demonstrated that that synesthesia can be trained, leading to exciting cognitive improvements. Although this was only temporary. Others believe that synesthesia develops as a response to learning challenges.
Non-synesthetes can also benefit from synesthesia. Synesthesia training may have implications to help older people slow their decline in cognitive functions. For example in early stage Alzheimers or helping patients recovering from brain injuries.
Perhaps people starting in their 50s could “top up” their memory when they use synesthetic colors. Such techniques could be a mnemonic device to remember shopping lists.
However, it seems that there are many benefits of having and training synesthesia. More science is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of synesthesia and memory improvement.
Symptoms of synesthesia – is it a disorder?
Synesthesia is not a disorder, nor is it a disease. And since only disorders and diseases can have symptoms, synesthesia does not have symptoms. Synesthesia is a perceptual experience. Consider it a gift.
For those who put synesthesia into the light of disorders and talk about symptoms, they may want to do their homework before engaging in any further discussion.
“Learn to meditate to experience synesthesia”
Of course, not everybody has synesthesia. But studies show that mediators are more likely to unfold their synesthetic abilities. Doing Mediation increases sensory sensitivity.
Synesthesia Meditation: sensory mindfulness and synesthetic explorations
Synesthesia Meditation helps you to become aware of your synesthetic abilities. As you practice 10 minutes per day you become familiar with techniques that help your to reconnect to your senses. And you will discover different types of synesthesia.
After a while, you will experience synesthesia in your daily life.
There are many documented benefits of mindfulness practice. Combining synesthesia and mindfulness has excellent potential for a significant variety of benefits and applications.
Why not start your journey now, for free? Check out the exercises in the gateway.
Practice Synesthesia Meditation
Or read about Synesthesia Meditation and its benefits.
Perceiving synesthesia – are you aware?
Synesthesia requires attention. Otherwise, you do not perceive it. There are many people with synesthesia, but many are not aware of it. Maybe you too?
There are several reasons why people are not aware of synesthesia.
The lack of attention is one and maybe the most important. Attention is crucial for perceiving synesthesia.
In this section, you will learn how attention modulates the synesthetic experiences.
If you want to learn more about why many people have a low mindful synesthetic awareness, click here and ready our article about mindful synesthetic awareness.
It is hard to put Synesthetic experiences in words and drawings
How is it to perceive Synesthesia?
Synesthetic colors can differ in “form, spatial arrangement, transparency, covering degree, intensity, and nuance” Some describe it as “Halo” or fog which surround the letter or number.
Describing synesthesia in words is not easy. Often the words in our language are not enough to explain synesthetic experiences to satisfaction.
Although it is very hard to express synesthetic perception in words, synesthetes can communicate to each other pretty well.
Every person with synesthesia perceives it differently but similar. They can resonate and understand what the other person is saying about their individual synesthetic experience.
Drawing synesthetic experiences is notoriously tricky.
You can zoom in and out of your synesthetic experience, consequently, it is hard to bring it on a 2-dimensional sheet. Drawing synesthetic experiences allows one to express the bigger concept of it. But seldom to depict it in detail.
Nevertheless, drawing is an excellent exercise to become fully aware of your sense of hearing. Why not try it out? Click here for a “drawing music” exercise.
Our attention modulates our perception
One critical aspect of synesthetic perception, or perception in general, is awareness. Awareness is to perceive consciously.
Only on what you shift your attention to, you become aware of. Sensations are all the unfiltered stimulations entering through the senses in our brain. Perception is what our attention filters out of it.
Our attention is like a flashlight in the dark. Imagine you are walking through a garden at night without moonlight. Where you point the beam of light onto, there you can see the flowers.
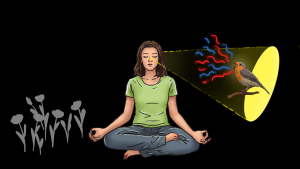
Your flashlight does not turn the night into day. It only has a narrow cone to illuminate the surrounding. But you can see quite well with it. Enough to navigate through the garden, seeing the flowers.
What happens to us is that we have our flashlight most of the time directed onto the path which we are walking. Well, that is important not to trip, but we should also not forget to lead them to the flowers that surround us.
And once we have a flower in our focus, we should not just switch back towards the path immediately. We should give it some time and look at the flower with all its beauty.
This metaphor describes nicely what happens to us. Our busy lives distract us from the perceptions of the present moment. Our mind tends to think constantly about the future and the past. And we miss the synesthetic experiences in our daily life.

With Synesthesia Meditation you gain a mindful synesthetic awareness to become more aware of synesthetic perceptions that surround you.

What do you see when you look into a river?
We can shift our attention to different aspects of perceptions and different synesthetic experiences.
Think about a river. When you go close to the river shore and look down, you can see the surface of the water. Maybe you see the sun that is reflected on it. Or you see the waves of the river.
Or you focus your sight on the river bed and you see the pebbles at the bottom.

Our attention modulates our perception. Shifting focus, zooming around, changes the way we perceive things.
In the same way, you can discover the synesthetic experiences within your perception. Your attention determines how the synesthetic perceptions unfold.
Shift your attention to different aspects of your synesthetic perception
Let’s consider music. Similarly to the river, you can shift your attention from one instrument to another. And you can observe its shapes and colors. Or you can zoom out and observe the overall picture of the music.
Or you focus on a single instrument and shift your attention between synesthetic types: from the shape of the sound to the movement to the color, to the surface, to the taste and back to the shape.
The same piece of music can be perceived differently every time. Your attention is never the same.
Such techniques are the groundwork of our sensory training in the sensorium.
In the Soundscapes, you find our Sound Series. It is a synesthetic Meditation that may help you to see music in shapes and colors. t
Try your free exercise about the colors of Music
Multisensory mechanisms: drivers in the evolution of language?
V. Ramachandran and E. Hubbard have proposed it, that synesthetic-like mechanism may play a role in the evolution of language.
Language may not have just emerged randomly. It may be that the shape of specific objects has induced the sound of words.
Let’s take the famous example below.

Almost everybody asked in this study had the same opinion, probably you have as well. Interestingly, people with autism tend to agree less than the overall population.
This multisensory perception is present in almost everybody, even in chimpanzees.
Such association with sounds exist not only for shapes, but it is also true for names.
Who do you think is thin and or fat? Kate or Molly?
Prevalence of Synesthesia
In a nutshell, we do not know exactly how prevalent synesthesia is. It could be between 1% and 25%. Diagnosing synesthesia is challenging. And depending on how to define what synesthesia is or not, there are more synesthetes.
“Diagnosing” Synesthesia is challenging
DISCLAIMER: If you have in mind to do one of our Synesthesia quizzes, you may do this before reading this paragraph.
Quick Quiz
Although there are different tools available, such as synesthesia tests, it is challenging to “diagnose Synesthesia.” The Gold Standard of “testing” for synesthesia is the consistency test.
Synesthetes tend to always perceive the same color for let’s say letters. And in this way, you can “test” for synesthesia. This method works fine but has its limits. Science can’t test all types of synesthesia like that.
Sometimes, synesthetes are classified as non-synesthetes. And vice versa.
Are there more females with synesthesia?
You can sometimes read that synesthesia is more common among women. But studies suggest that the ratio between female and male synesthetes is more or less the same.
Though women tend to be generally more interested in this topic than men. Similarly as you find also more females in a yoga class.
The Prevalence of synesthesia – how frequent is it?
As mentioned, the prevalence of synesthesia is estimated to be somewhere between 1% and 25%.
Yes, you may be now disappointed by this very imprecise answer, since this is quite a wide range. It is not so easy to figure out how common synesthesia is. So let me explain.
Prevalence estimations are constantly rising.
The estimated prevalence of synesthesia has continuously increased the past 30 years.
Another study had a look on art school students in Switzerland. They found out that the prevalence of synesthetes is higher in artistic schools with around 7% compared to 2% in regular schools.
A new study with students in Canada and Czech found that around 2% resp 4.4% had at least one type of synesthesia. They claim that it is an underestimate.
One researcher proposed that 20% of the population had Calendar Synesthesia.
And to add some more confusion, a study from 2016 used questionnaires, but not the typical consistency test. They came up with a 25% estimation. This would mean, every fourth person on this planet has at least one type of synesthesia. But the authors of this study admit themselves, that it is an overestimation.
You see, there is not yet an agreement how common synesthesia is precise. There is definitively a trend from “a rare phenomenon” to something that may be much more common than we assumed the last 30 years.
Our guesstimate of the prevalence of synesthesia is around 10%.
We need more studies! It won’t be easy to figure out the exact number. Please do not cite us on the 10%.
What is actually much more important is the following:
Synesthesia is common.
And you may have it. And you may be unaware of it.
But why is it so hard to come up with accurate estimations?
If you want to learn more about the testing of synesthesia and its prevalence, read the section in “science of synesthesia” or “Prevalence of Synesthesia.”
Social exchange is important to become aware
In the end, it does not matter for you to know the exact prevalence score. More important is that you know that there are many synesthetes out there. And many do not know about it.
Ask your friends and family members!
Maybe they see letters and numbers in colors. Or music in shape. Do not talk about synesthesia as if it was something weird or overly special. It is a very common phenomenon. Go out, help other people as well to discover their synesthetic sensory abilities.
To give you a guide how to approach other people to exchange about synesthesia, read our article about synesthetic mindful awareness.
A conclusion of what synesthesia is.
Synesthesia is perceiving the world with blended senses in the here and now.
There are many people with synesthesia, but most are not aware of it. Slowly we realize, that it is more common than assumed. And many are not aware of it. Maybe you too?
We, the team of Synesthesia.com, have spent several years to find a solution to that problem. We aim to support people on their journey to become aware of synesthesia.
Synesthesia Meditation in the Sensorium is our approach. It is a mix of mindfulness techniques and synesthetic exploration.
Connect with your senses and become aware of synesthesia. It is an investment in your mind and you overall life quality. There are many benefits of Synesthesia Mediation, such as more sensory awareness, less stress and anxiety, more calm, patience and focus. It is really worth the time.
Practice 10 minutes a day and discover the full range or your synesthetic abilities.
Read more hear about synesthesia here on the Blog. Or start directly for free in the Gateway, where you find many free exercises that are just one click away.
Free ExercisesWhat to do next?
Watch our Video about synesthesia Meditation
Learn more about how the Sensorium works.
Synesthesia Meditation – synesthetic Mindfulness for sensory Awareness
Guided Synesthesia Meditation is a combination of mindfulness exercises and synesthetic explorations. Practice 10 minutes per day. Increase your synesthetic mindfulness* and sensory awareness. Find better sleep, increase feelings of calm, relaxation and balance, while decreasing stress, and gaining improved focus and life quality. Over 150 exercises are available on https://synesthesia.com.

